Art Overview
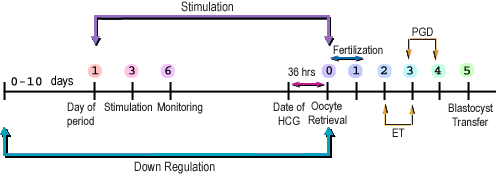
Stages of the ART cycle
Whatever be the ART procedure, every cycle will consist of the following stages:
- Controlled Ovarian Stimulation
- Monitoring
- The Oocyte Retrieval
- The Laboratory Procedure
- Embryo Transfer
- Cryopreservation
1. Controlled Ovarian Stimulation:
The aim of this step is to achieve a higher rate of pregnancy for which the woman's menstrual cycle is administered. Usually, a woman produces one mature egg during her menstrual cycle. In ART, we aim at initiating the production of several eggs so that several embryos are produced. Only the best out of them will be inserted in the womb. This is achieved with the help of special drugs called gonadotrophins that are administered by making use of the following regimes or protocols:
a. The Long protocol--Luteal phase suppression with stimulation.
1. This is the most common protocol used in ART. The patient is put on the GnRh analogue (Lupride, Decapeptyl, Suprefact) subcutaneously, which starts 7 days prior to the expected menses and is continued throughout the menses and subsequently for 12 days more. This drug may be given daily, in a predetermined dosage, with a disposable Insulin syringe.
Dosage:
Half ml, equivalent to 20 units of an Insulin syringe, is given every day. Generally an ampoule of Suprefact contains 6 ml of the drug. Alternately a single shot of Decapeptyl, Depot or Zoladex can be given on the 21st day of the previous cycle.
2. A blood test for Estradiol hormone may be done on the 2nd day of menses to confirm suppression. Generally, the count should be less than 50. A sonography scan is done to rule out any fluid retention in the ovary (cyst) and to assess the uterus lining. Ideally, its thickness should be less than 4 mm. In case there is a pre-existing ovarian cyst, Transvaginal Aspiration may be carried out, prior to the stimulation phase. Once this is achieved, the actual ovarian stimulation is started by making use of special hormones called Gonadotrophins
Stimulation With Gonadotrophins
The Gonadotrophins are started from 2nd day of the menstrual period.
Stimulation is initiated with one of the following drugs:
HMG (Pergonal,Humegon,Menogon,GMH)
FSH (Metrodin, Metrodin HP)
Fostine
Endogen
GonotropC,Puregon or Recombinant FSH (Gonal F or Recagon)
Normally FSH or Recombinant FSH (dosage being 150 to 300 units per day) is used for the first 3 to 6 days followed by HMG (dosage being 150 to 300 units per day) for the next 8 to 5 days. The dosage varies, depending on the age of the patient, and the response of ovaries to stimulation.
b. The short protocol
This is similar to the long protocol. However in this regime, the Suprefact is started from the 2nd day of the cycle, and is continued for 12 days, till the ovulating dose of HCG is given
c. The ultrashort protocol
In this regime, the GnRh analogue (Suprefact) is given from the 2nd day till the 5th day of the cycle. The rest is similar to the long protocol. Generally this regime is given to elderly patients or to poor responders, who are known to have a very low egg count.
2. Monitoring
The administration of gonadotrophins results in the formation of multiple bags of water in the ovaries, called follicle. Each follicle has within itself, an egg or oocyte. The number and size of the follicles is monitored with the help of serial Vaginal sonography and Estradiol hormone estimation. The dose of gonadotrophins is increased or maintained, based on follicular growth and rise of estradiol hormone. When the two leading follicles are in the range of 17 to 18 mm diameter, the patient is ready for the final administration of HCG hormone. The patient is injected deep intramuscularly with HCG in the dose of 5000 to 10000 Iu. The timing of the injection is very important. The ovum pickup or the egg retrieval is done 35 to 37 hours after the HCG injection.
3. The Oocyte Retrieval
The oocyte retrieval is done 35 to 37 hours after the maturation injection of HCG. This is a day care outpatient procedure. It may be carried out either under local anesthesia or general anesthesia. We prefer to do it under short general anesthesia, using the latest probofol anesthesia, which has minimal side effects.
Procedure:
The whole procedure takes about half an hour and the patient can go home in 4 hours time. The patient shall be asked to skip dinner and get admitted an hour prior to the ovum pickup. It is important to remember not to shave the genitalia. The egg retrieval is done with the aid of vaginal ultrasound machine. A thin sonography probe is passed into the vagina. The aspiration needle is passed through a channel guide attached to the probe. The needle is passed into the follicle puncturing the vaginal wall.
The sperm retrieval: Normally, the semen is collected by masturbation 1-2 hours after egg collection. The husband is given a sterile container, asked to wash his hands prior to collecting the sample. It is important not to wash the penis.
Semen Production In case the husband has previous history of difficulty in producing semen, we ask him to produce the semen a few days earlier and freeze it, for subsequent use. In case the husband requires his partner for semen production, he is asked to produce the sample, prior to egg collection. If he cannot produce the semen in the hospital, he shall be given a sterile container to produce the semen at home and bring it to the hospital. If that fails then he is given a mechanical vibrator to produce the same.
Procedures for Semen Retrieval
When all of the above methods fail, the patient will be anesthetized for a procedure of electro-ejaculation. During this procedure, a probe is passed in to the rectum, and stimulation is given, which results in automatic ejaculation of semen.
Alternatively, a surgical testicular biopsy (PESA,MESA or TESE) may be done to retrieve sperms and fertilise eggs using the procedure of ICSI. This is done in patients with azoospermia or for those who fail to produce semen on the day of egg retrieval.
Fertilization:
The eggs, which are retrieved by aspiration, are then washed with special culture media and kept in incubators. Similarly, the sperms that are obtained are washed with culture media, with the standard swim up method. In case of oligospermic samples, they may be washed using the density gradient method.
Depending upon the sperm counts and the egg quality, fertilization methods will be different. In case of normal sperm counts, fertilization is achieved by IVF . In case of low sperm counts, fertilization is achieved by the process of ICSI.
5. Embryo Transfer:
This is one of the most important steps. The transfer of the selected cleaved embryos is performed 48 hours after the initial egg collection.
Procedure:
- A fine catheter is inserted through the cervix, via the vagina, to reach high into the uterus.
- The embryos, resting in a minute amount of culture medium, are then injected though the catheter and passed out into the uterus(womb).
- This procedure is of a very short duration and does not usually require any form of sedation.
Cryopreservation:
Suitable embryos not utilised during the transfer may be cryo-preserved (frozen) for use in another treatment cycle, if desired. These embryos are mixed with special media called cryprotectant. The embryos are loaded into straws, which are then sealed and placed in a special machine called an-Freezer. The machine is programmed by computers to pull down the temperature slowly at the rate of 0.3 degrees centigrade. Till the temperature falls down to minus 79 degrees. The straws are then stored in Liquid nitrogen containers, which are at a temperature of minus 196 degree centigrade.
Once the embryo reaches the uterus, it may float around for 2-3 days, still growing. It does not stick to the lining of the uterus until about 7 days after fertilization, when the process of implantation starts.
By this time the embryo, now known as the Blastocyst, will have two distinct types of cells: one type will form the afterbirth (known as the placenta) and the other will form the fetus. The embryo begins burrowing into the endometrium and the placenta starts to form - a pregnancy is achieved. At this stage, the placenta starts to produce the pregnancy hormone (human chorionic gonadotropin - hCG). Implantation of the embryo is the attachment of the embryo to the endometrium (lining of the womb). It occurs about a week after fertilization; and is a very delicate and complex process. This hCG will continue to stimulate the corpus luteum so that progesterone production is maintained and the pregnancy can continue. The corpus luteum is functional for the first 8 weeks of pregnancy then the progesterone production is taken over by the placenta.
At an advanced stage of embryo development, the embryo consists of an outer thin layer of cells, which later develops to placenta and an inner cell mass which later develops to fetus.
We already know that with natural conception, embryos arrive in the uterus at day 5-6 after fertilization. With present-day IVF, however, embryos are routinely transferred back to the uterus on day 3 after fertilization. Recent breakthroughs have been made in the science of nurturing embryos in the laboratory. These discoveries have allowed the embryos from select patients to benefit from an additional 2 to 3 days of growth prior to embryo transfer.
By growing embryos to the Blastocyst stage, we are able to transfer fewer embryos without lowering the chance that a patient will become pregnant. This breakthrough will help maintain the high pregnancy rates that patients have come to expect while decreasing the risk of conceiving a high order multiple pregnancy.